Retina is an extension of the brain. Much like the brain tissue, retina cannot regenerate –diseases of the vitreous and retina can cause permanent blindness. Prompt and appropriate treatment can halt further damage and result in better outcome. Retinal examination allows early detection and treatment of retinal disorders. Who need retina check up?
Those who has systemic complaints (diabetes, hypertension), high myopia, eye injury, family history of retinal detachment, black spots problem, Flashes of light, new or increase in floaters [ black dots in your vision ], A gray curtain noticed in the field of vision, night blindness. Retinal Exam
The exam includes a complete ophthalmic assessment from the front of the eye to the back of the eye.
THE RETINAL EXAM INCLUDES :
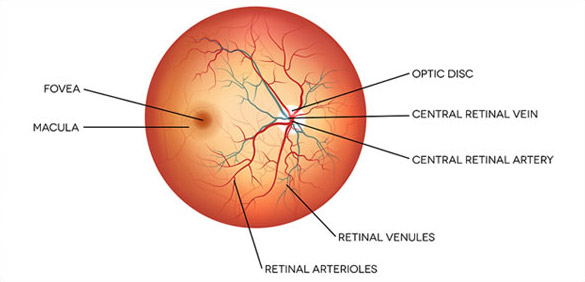
- A full inspection of the vitreous cavity and examination of the optic nerve, macula, retinal blood vessels and extreme peripheral retina.
- Once this is done, your doctor will make the decision whether or not to perform various retinal tests to further clarify the vitreous, macula, retina or choroidal diagnosis.
PROCEDURE FOR A RETINAL CHECK UP :
First through a routine check up of your refraction. This will be followed by dilatation of your pupils for a detailed retinal exam by a consultant.
Precautions for a retinal check up
Following dilatation, it may be difficult to read or drive for several hours after the visit. If you have other systemic complaints ( diabetes, hypertension etc ), bring in your other medical records with details of the medications you are on.
- Vitreo-retinal problems
- Retinal Detachment
- Macular Degeneration
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Age-related macular degeneration
Medical Treatment
The goal of most treatments is to stop disease progression and preserve or improve vision.
- Green Laser Therapy (Focal Laser Photocoagulation): To repair a Diabetic Retinopathy, Eales Disease, Retinal Tears and other Retinal Diseases. Scatter laser treatment (panretinal photocoagulation). This laser treatment often can shrink abnormal new blood vessels that are bleeding into the vitreous in diseases such as diabetic retinopathy.
